Medicaid vs Medicare Differences
When it comes to healthcare coverage, understanding the differences between Medicaid and Medicare is crucial.
This article directly compares eligibility, coverage options, and costs to help you determine which program aligns with your needs. Navigate the complexities of ‘medicaid vs medicare’ with our straightforward guide, designed to empower your healthcare decisions without overwhelming detail.
Key Takeaways
- Medicare is federally-funded for seniors 65+ and individuals with certain disabilities, with coverage split into Parts A, B, C, and D, whereas Medicaid is state-funded, aiding low-income people of all ages with a broad range of services including long-term care.
- Eligibility for Medicare is based on age or disability, with costs including premiums, co-pays, and deductibles; Medicaid eligibility is income-based with minimal out-of-pocket expenses, making it affordable for low-income individuals.
- Dual eligibility allows qualified individuals to receive combined benefits from Medicare and Medicaid, maximizing coverage and minimizing personal healthcare expenses.
Compare Plans in One Step!
Enter Zip Code
Medicaid vs Medicare: A Comprehensive Comparison
Medicare and Medicaid are two prominent health insurance programs in the United States. The federal health insurance program Medicare is mainly for people aged 65 or older.
It also provides coverage for certain younger individuals with disabilities and those with End-Stage Renal Disease.
On the other end of the spectrum, Medicaid is a state program designed to assist Americans of all ages with limited income, covering their medical and long-term custodial care expenses.
Eligibility Criteria
The eligibility requirements for these programs are quite distinct. Medicare eligibility primarily hinges on age or disability, with individuals who are 65 or older, certain younger people with disabilities, and people with End-Stage Renal Disease qualifying for this health insurance program. On the other hand, Medicaid is primarily for low-income Americans of all ages, with specific income thresholds determined by each state.
Consequently, while Medicare is more age-focused, Medicaid centers on financial need.
Coverage Offered
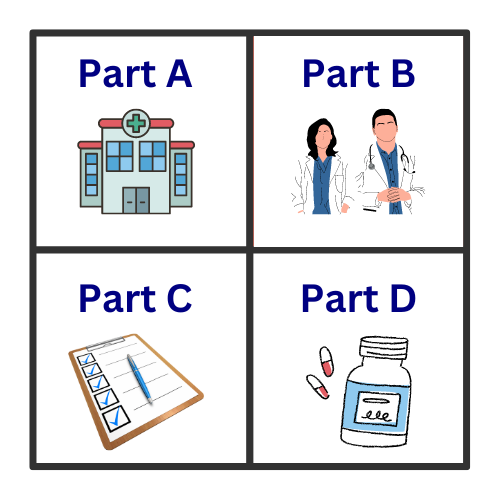
These programs also differ in the coverage they offer. Medicare provides coverage through its four parts:
- Part A covers hospitalization
- Part B covers medically necessary services and equipment
- Part C, known as Medicare Advantage, includes additional benefits
- Part D provides prescription drug coverage.
On the contrary, Medicaid offers a diverse range of services, including preventive services, which are not typically covered by Medicare.
This extensive coverage, coupled with its role as the primary payer of long-term care in the United States, makes Medicaid a vital lifeline for many low-income individuals and families.
Costs and Premiums
These programs have distinct cost structures. Medicare enrollees are responsible for their coverage costs, which include monthly premiums, co-pays, and deductibles.
Conversely, Medicaid recipients typically incur minimal to no out-of-pocket expenses, as it helps cover medical costs, making it a more affordable option for those with limited financial resources and reducing their overall medical costs.
Medicare Advantage Plan Enrollment
If you are new to Medicare, the best time to enroll in a Medicare Advantage plan is between the time period three months prior to turning age 65, your birthday month, and three months after your 65th birth month. This is what is called your “Initial enrollment period”.
Your coverage will begin on the first of the month after the date that you sign up during your INITIAL ENROLLMENT PERIOD.
Already enrolled in Medicare?
If you are already enrolled in Medicare and want to enroll in a Medicare Advantage plan (also called Medicare Part C), then you can switch and enroll in one during the Medicare Annual Enrollment period. This period runs between October 15th and December 7th of every year.
Your coverage will then begin on January 1st of the following year.
Medicare Breakdown: Understanding Parts A, B, C, and D
Having outlined the distinctions between Medicaid and Medicare, we can now examine Medicare in more detail. Comprised of four parts – A, B, C, and D – Medicare offers a diverse range of coverage options, each with its own unique set of benefits and costs. A thorough understanding of these components can help eligible individuals choose a plan that best meets their needs.
Part A: Hospital Insurance
Medicare Part A, often referred to as hospital insurance, covers:
- Inpatient hospital care
- Skilled nursing facility care
- Hospice care
- Home health care
This coverage is typically provided without a premium for most enrollees who have paid Medicare taxes while working. Thus, for those eligible, Part A offers a robust safety net for hospital-related expenses.
Part B: Medical Insurance
Complementing Part A is Medicare Part B, which covers medically necessary services and equipment. This includes:
- Clinical research
- Ambulance services
- Durable medical equipment
- Mental health services
- Outpatient care
Unlike Part A, Part B does come with a standard premium, which is either $278 or $506 each month, depending on the individual’s or their spouse’s work history and payment of Medicare taxes.
Part C: Medicare Advantage Plans
Medicare Part C, also known as Medicare Advantage, provides an alternative method for receiving Original Medicare benefits along with additional coverage. These plans are offered by private insurance companies approved by Medicare and may include supplementary benefits such as vision, dental, and hearing services, which are not typically covered by Original Medicare.
Medicare supplement insurance can be an option for those looking for additional coverage beyond what Medicare Advantage offers.

Though, it should be noted that depending on the Medicare Advantage plan and services used, Medicare Advantage plans might result in higher out-of-pocket expenses for some individuals.
Part D: Prescription Drug Coverage
Last but not least is Medicare Part D, which offers prescription drug coverage for various prescription drugs. The costs associated with Part D depend on the chosen plan, and enrollees are responsible for monthly premiums, an annual deductible, and out-of-pocket copayments for specific prescriptions.
Comprehending the details of Part D is especially important for individuals who require regular medication, given its potential to significantly affect out-of-pocket healthcare costs.
Navigating Medicaid: Eligibility, Benefits, and Application Process
Let’s switch our focus and examine Medicaid more closely. As a state-dependent program, understanding the nuances of Medicaid can be a bit more complicated but is equally important, especially for low-income individuals and families who depend on this program for their healthcare needs.
State-Specific Eligibility
One of the key aspects to grasp about Medicaid is its state-specific eligibility criteria. While Medicaid is a joint federal and state program, the income and resource rules that determine qualification can vary significantly from one state to another. Thus, it’s important to understand the specific requirements in your state of residence to ascertain eligibility.
Benefits and Services
Medicaid’s benefits include a wide array of services. In addition to federally mandated coverage such as inpatient and outpatient hospital services, physician services, and family planning, Medicaid may offer additional state-specific coverage options.
This extensive coverage, including long-term care services and mental health services, varies depending on the state and the specific services needed.
Applying for Medicaid
There are several key steps involved in applying for Medicaid. These include:
- Identifying the type of Medicaid needed
- Assessing potential automatic eligibility
- Gathering required supporting documents
- Reaching out to the state’s Medicaid office for specific application guidelines.
Thankfully, the option to apply for Medicaid online is available and can offer added convenience for certain applicants.
Dual Eligibility: Combining Medicare and Medicaid Coverage
In some circumstances, individuals might be eligible for both Medicare and Medicaid, a condition referred to as dual eligibility. This enables individuals to access the combined coverage offered by these two programs, providing a more comprehensive safety net for healthcare costs.
What It Means to Be Dually Eligible
Dual eligibility refers to an individual’s qualification for both Medicare and Medicaid. This dual eligibility not only provides a more comprehensive coverage but also lessens out-of-pocket expenses, making healthcare costs more manageable for those with limited financial resources.
Coordinating Benefits
Coordinating benefits between Medicare and Medicaid enables plans to:
- Assess the coverage for an individual with both Medicare and Medicaid
- Identify the health benefits available
- Coordinate the payment process
- Ensure claims are paid correctly.
Making the Right Choice: Tips for Selecting the Best Health Coverage Option
After examining the details of Medicare and Medicaid, the final step involves evaluating your individual needs and making an informed health coverage decision. Here are some tips to guide you in this process.
Assessing Your Needs
Assessing your needs is the first step in choosing a health coverage plan. This includes:
- Understanding your financial situation
- Understanding your healthcare needs
- Determining your eligibility for Medicare and/or Medicaid
- Considering potential chronic health conditions that may necessitate more comprehensive healthcare coverage.
Seeking Expert Advice
After evaluating your needs, seeking expert advice is a good next step. Certified Medicaid planners and Certified Application Counselors are trained and certified to provide accurate and up-to-date advice on eligibility, coverage options, enrollment, and other program-specific details.
Government resources such as the official Medicare and Medicaid websites can also provide valuable information.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding the differences between Medicaid and Medicare is key to making informed decisions about health coverage. While both programs aim to support individuals in accessing healthcare, they cater to different populations and offer distinct benefits and costs.
By comprehensively understanding these programs – from eligibility criteria to coverage options and costs – individuals can select the plan that best suits their needs and financial situation.
Frequently Asked Questions
→ What is the difference of Medicare and Medicaid?
The main difference between Medicare and Medicaid is that Medicare is for individuals aged 65 and older, or those with disabilities, regardless of income, while Medicaid provides health coverage for people with very low incomes. These programs are designed to provide health insurance to different segments of the population.
→ What is the lowest income to qualify for Medicaid?
To qualify for Medicaid, low-income adults with no children typically need to make less than 138% of the Federal Poverty Level (FPL) or $17,226 per year if they are the only person in their household. The FPL is determined by the size of the family.
→ Do you pay for Medicare?
Most people get Medicare Part A for free, but some may have to pay a premium depending on their eligibility. The total costs for all Medicare coverage typically range between $175 and $371 per month, but this can be lowered based on income.
→ Who is eligible for Medicaid and Medicare?
If you are 65 or older, have certain disabilities, or have End-Stage Renal Disease, you are eligible for Medicare. Medicaid is available to low-income individuals of all ages, with income thresholds varying by state.
→ What does Medicare Part C, also known as Medicare Advantage, cover?
Medicare Part C, also known as Medicare Advantage, covers Original Medicare benefits along with additional coverage such as vision, dental, and hearing services through private insurance companies.

ZRN Health & Financial Services, LLC, a Texas limited liability company
Russell Noga is the CEO of ZRN Health & Financial Services, and head content editor of several Medicare insurance online publications. He has over 15 years of experience as a licensed Medicare insurance broker helping Medicare beneficiaries learn about Medicare, Medicare Advantage Plans, Medigap insurance, and Medicare Part D prescription drug plans.




